
- How to format disk windows 10 wioth command prompt how to#
- How to format disk windows 10 wioth command prompt full#
- How to format disk windows 10 wioth command prompt windows 10#
How to format disk windows 10 wioth command prompt windows 10#
You may like: Relocate Installed Apps and Games in Windows 10 Format USB Drive on Windows 10 using Command prompt In some cases, using the command line can help but it may not necessarily help in every situation. Furthermore, a formatting error can occur due to a number of reasons. If you have any important data saved to the drive make sure you copy or move it to a safe place. Note: Formatting a USB Drive will erase all data on it. Just follow the instructions given below and by the end of it, you’ll realize it too. However it may seem, using the command line is pretty simple and in some cases simpler than using the GUI.
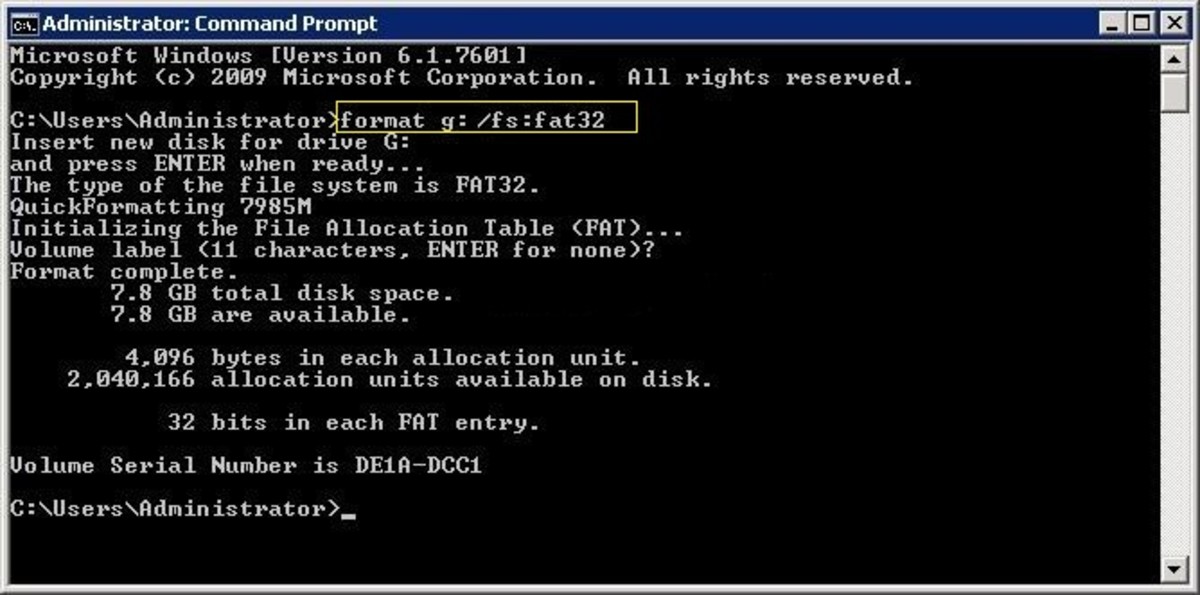
Using the command line seems like a job only programmers and computer wizards would do. You don’t know what to type, and even when you do know you can’t make sense of it. Most Windows users will probably shy away from the command line because it seems like a daunting task. So if you’re facing any such errors while trying to format USB drive on Windows 10 you can try the command prompt. Usually, when a GUI method fails, there’s a command line method to do the same thing which probably won’t fail. In most cases, the error message you’re shown is Windows was unable to complete the format. Sometimes though, this method can return an error. You get to select a new file system for the drive before you click the Start button and that’s it. It’s fairly straightforward and all you have to do is right-click on it and select Format.
How to format disk windows 10 wioth command prompt how to#
So it’s still a work-in-progress product that will come around later.If you’ve been a Windows user for even a small amount of time, you’d know how to format USB Drive on Windows. x, /clearDefault do not display the default selected columnsĭiskUsage is only available in Windows Insider builds, 21277 and above. v, /verbose displays verbose error information u, /TopFile=N displays Top N files by SizeOnDisk in descending order t, /TopDirectory=N displays Top N directories by SizeOnDisk in descending order
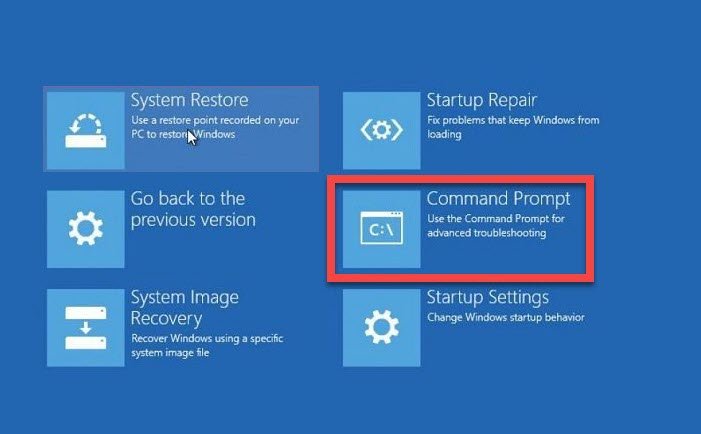
s, /skipResurse skip recursing into child directories when calculating sizes

r, /skipReparse skip recursing into reparse directories q, /virtual recurse into virtual directories NOTE: This options must not be specified togerther p, /preferredPath=PATH count files with multiple link names towards the first link that's n, /nameFilter=FILTER count only files whose name matches the name filter m, /multipleName count only files with more than one link names Hardlinks are counted only once towards the first link name) l, /allLinks count all hardlinks separately (By default, files with multiple j, /secnario=SCENARIO specifies the scenario name for the INI file NOTE: SCENARIO name must be speificed via /j (/scenario) i, /iniFile=FILE takes all the parameters from an INI file. h, /humanReadable displays size in human readable format LastWriteTime 0x200 file last write timestamp LastAccessTime 0x100 file last access timestamp SizePerDir 0x004 sum of SizeOnDisk for top level childĬhildDirs 0x010 number of child directoriesįilesPerDir 0x020 number of top level child filesĭirsPerDir 0x040 number of top level child directoriesĬreationTime 0x080 file creation timestamp g, /displayFlag=FLAG specifies the flags value to determin which column(s) to display f, /minSizeOnDisk=SIZE displays directory information only if its SizeOnDisk e, /minFileSize=SIZE displays directory information only if its FileSize d, /maxDepth=N displays directory information only if it is N or a, /systemAndReserve displays size for system files and reserved space C:\WINDOWS\system32>DiskUsage /?ĭescription: Summarize disk usage recursively for the given directory.
How to format disk windows 10 wioth command prompt full#
To find the full usage of the command line, use /?. There is also a switch /h to display sizes in human-readable format rounded to gigabytes, as well a switch /c as /csv to display the result in CSV format.Īnd at the end of the result, DiskUsage always provides used vs total size with a percentage of how much disk space in use.
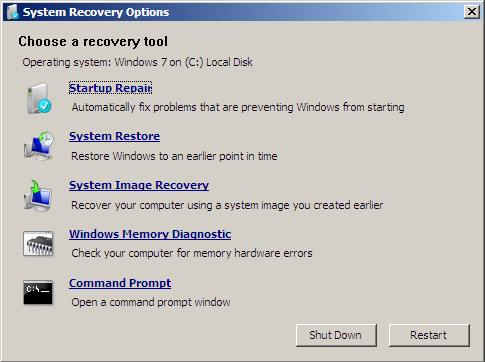
DiskUsage įor example, to find all files that are larger than 1GB in my windows folder. To use the command line, open an elevated command prompt or PowerShell window and type the following command. DiskUsage is an up-coming command-line in Windows that checks and summarize disk usage recursively for the giving directory. Now Windows is going to have a native one shortly in the future. To fill the gap in Windows, Sysinternals provides a similar command-line tool, du, that reports the disk usage for the directory you specify. Linux has du, a standard command-line that allows a user to check the disk usage information quickly.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
